How To Set Up Visual Studio Code For C++
Using GCC with MinGW
In this tutorial, yous configure Visual Studio Lawmaking to employ the GCC C++ compiler (grand++) and GDB debugger from mingw-w64 to create programs that run on Windows.
After configuring VS Code, you will compile and debug a elementary Hello World program in VS Lawmaking. This tutorial does not teach you about GCC, GDB, Mingw-w64, or the C++ language. For those subjects, there are many good resources available on the Web.
If y'all take any bug, feel free to file an effect for this tutorial in the VS Lawmaking documentation repository.
Prerequisites
To successfully complete this tutorial, you must practise the following steps:
-
Install Visual Studio Code.
-
Install the C/C++ extension for VS Code. You tin install the C/C++ extension by searching for 'c++' in the Extensions view ( ⇧⌘Ten (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X)).

-
Go the latest version of Mingw-w64 via MSYS2, which provides upwardly-to-date native builds of GCC, Mingw-w64, and other helpful C++ tools and libraries. You tin download the latest installer from the MSYS2 folio or use this link to the installer.
-
Follow the Installation instructions on the MSYS2 website to install Mingw-w64. Take care to run each required Starting time bill of fare and
pacmancommand, especially Step 7, when you volition install the actual Mingw-w64 toolset (pacman -South --needed base of operations-devel mingw-w64-x86_64-toolchain). -
Add the path to your Mingw-w64
binfolder to the WindowsPATHsurround variable by using the following steps:- In the Windows search bar, type 'settings' to open your Windows Settings.
- Search for Edit environment variables for your account.
- Choose the
Pathvariable in your User variables and then select Edit. - Select New and add together the Mingw-w64 destination folder path to the system path. The exact path depends on which version of Mingw-w64 you have installed and where you installed it. If you used the settings above to install Mingw-w64, so add this to the path:
C:\msys64\mingw64\bin. - Select OK to save the updated PATH. You will need to reopen any console windows for the new PATH location to be available.
Check your MinGW installation
To check that your Mingw-w64 tools are correctly installed and available, open a new Control Prompt and type:
g++ --version gdb --version If you don't come across the expected output or g++ or gdb is not a recognized command, brand sure your PATH entry matches the Mingw-w64 binary location where the compilers are located. If the compilers exercise not be at that PATH entry, brand sure you followed the instructions on the MSYS2 website to install Mingw-w64.
Create Hi World
From a Windows command prompt, create an empty folder called projects where yous can place all your VS Code projects. And so create a sub-folder called helloworld, navigate into information technology, and open VS Lawmaking in that folder by entering the following commands:
mkdir projects cd projects mkdir helloworld cd helloworld code . The "lawmaking ." command opens VS Code in the current working folder, which becomes your "workspace". Accept the Workspace Trust dialog by selecting Yeah, I trust the authors since this is a folder you created.
As you become through the tutorial, you will meet three files created in a .vscode binder in the workspace:
-
tasks.json(build instructions) -
launch.json(debugger settings) -
c_cpp_properties.json(compiler path and IntelliSense settings)
Add a source code file
In the File Explorer championship bar, select the New File push and name the file helloworld.cpp.

Add hello world source code
Now paste in this source lawmaking:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> using namespace std ; int principal () { vector<string> msg { "Hi" , "C++" , "Earth" , "from" , "VS Code" , "and the C++ extension!" }; for ( const cord& discussion : msg) { cout << word << " " ; } cout << endl; } At present press ⌘South (Windows, Linux Ctrl+S) to salvage the file. Observe how the file you just added appears in the File Explorer view ( ⇧⌘E (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+East)) in the side bar of VS Code:
Yous can also enable Machine Save to automatically save your file changes, by checking Auto Save in the main File carte.
The Activity Bar on the far left lets you open different views such as Search, Source Control, and Run. You'll expect at the Run view later on in this tutorial. Yous tin find out more about the other views in the VS Code User Interface documentation.
Note: When you relieve or open a C++ file, you may come across a notification from the C/C++ extension about the availability of an Insiders version, which lets you test new features and fixes. You tin ignore this notification by selecting the
X(Clear Notification).
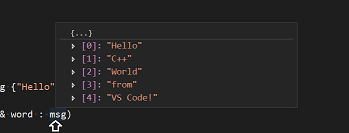
Explore IntelliSense
In your new helloworld.cpp file, hover over vector or cord to run across blazon information. After the declaration of the msg variable, start typing msg. as you would when calling a member function. You should immediately come across a completion list that shows all the member functions, and a window that shows the type information for the msg object:
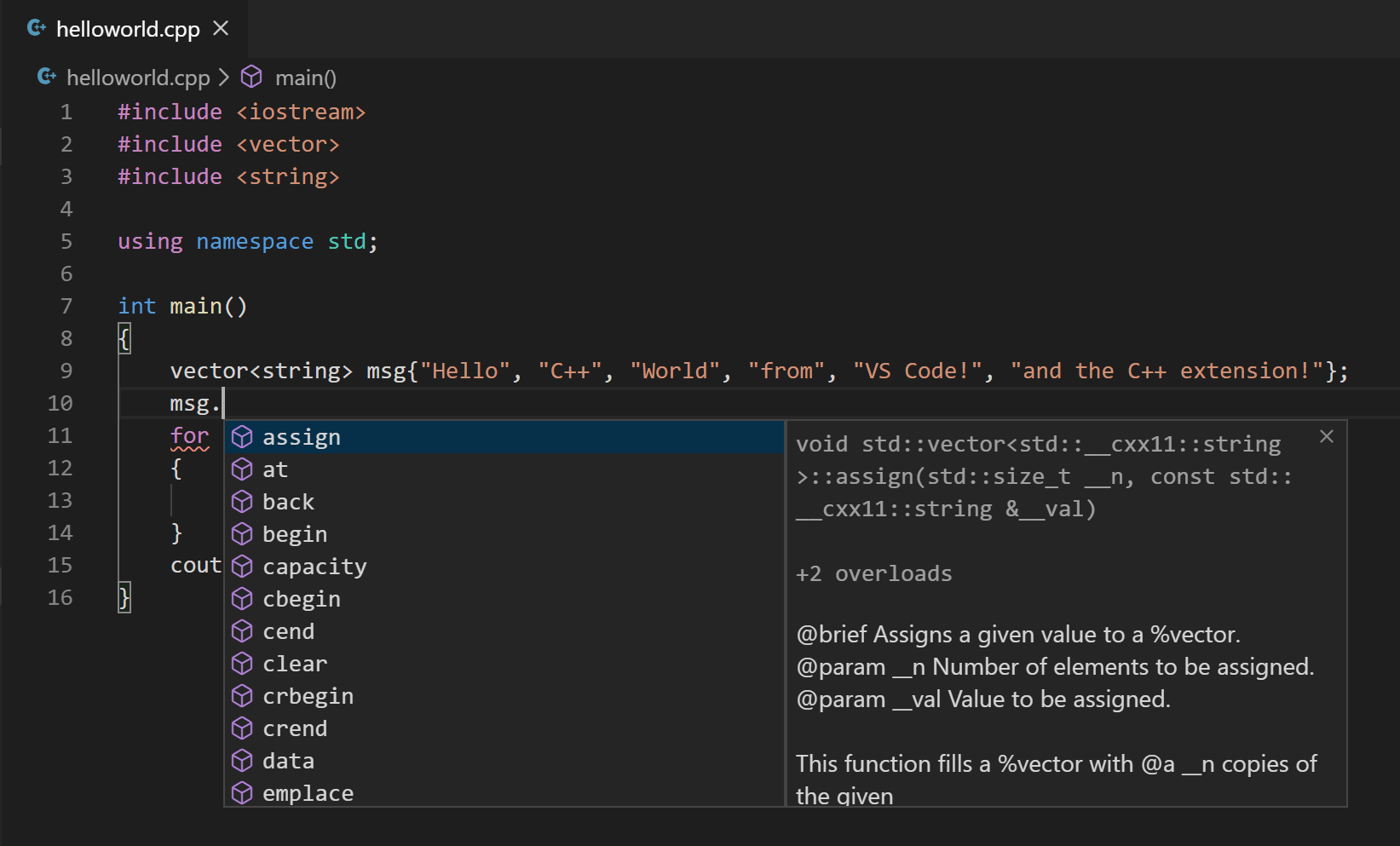
You lot tin press the Tab central to insert the selected member; then, when you add the opening parenthesis, you will encounter information about any arguments that the function requires.
Build helloworld.cpp
Next, you'll create a tasks.json file to tell VS Code how to build (compile) the plan. This task volition invoke the g++ compiler to create an executable file based on the source code.
From the primary menu, choose Concluding > Configure Default Build Job. In the dropdown, which will display a tasks dropdown listing various predefined build tasks for C++ compilers. Cull m++.exe build active file, which will build the file that is currently displayed (active) in the editor.
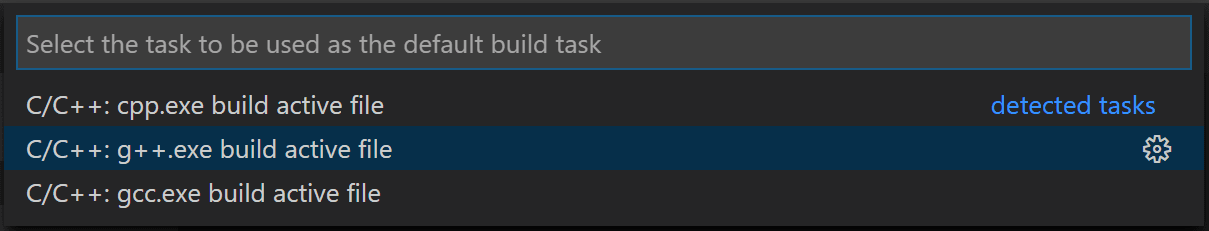
This volition create a tasks.json file in a .vscode folder and open it in the editor.
Your new tasks.json file should wait like to the JSON below:
{ "tasks" : [ { "blazon" : "cppbuild" , "label" : "C/C++: g++.exe build agile file" , "command" : "C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/g++.exe" , "args" : [ "-m" , "${file}" , "-o" , "${fileDirname} \\ ${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe" ], "options" : { "cwd" : "${fileDirname}" }, "problemMatcher" : [ "$gcc" ], "group" : { "kind" : "build" , "isDefault" : true }, "detail" : "compiler: C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/thou++.exe" } ], "version" : "2.0.0" } The control setting specifies the program to run; in this example that is chiliad++. The args assortment specifies the command-line arguments that will be passed to g++. These arguments must be specified in the club expected by the compiler. This task tells g++ to have the active file (${file}), compile information technology, and create an executable file in the current directory (${fileDirname}) with the same name as the active file but with the .exe extension (${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe), resulting in helloworld.exe for our example.
Notation: Y'all can acquire more about
tasks.jsonvariables in the variables reference.
The label value is what you will see in the tasks listing; y'all tin proper noun this whatever you like.
The "isDefault": true value in the group object specifies that this task volition be run when you press ⇧⌘B (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+B). This property is for convenience but; if y'all set it to false, you lot can still run it from the Final carte du jour with Tasks: Run Build Job.
Running the build
-
Go back to
helloworld.cpp. Your task builds the active file and you desire to buildhelloworld.cpp. -
To run the build job divers in
tasks.json, printing ⇧⌘B (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+B) or from the Terminal main menu choose Run Build Chore. -
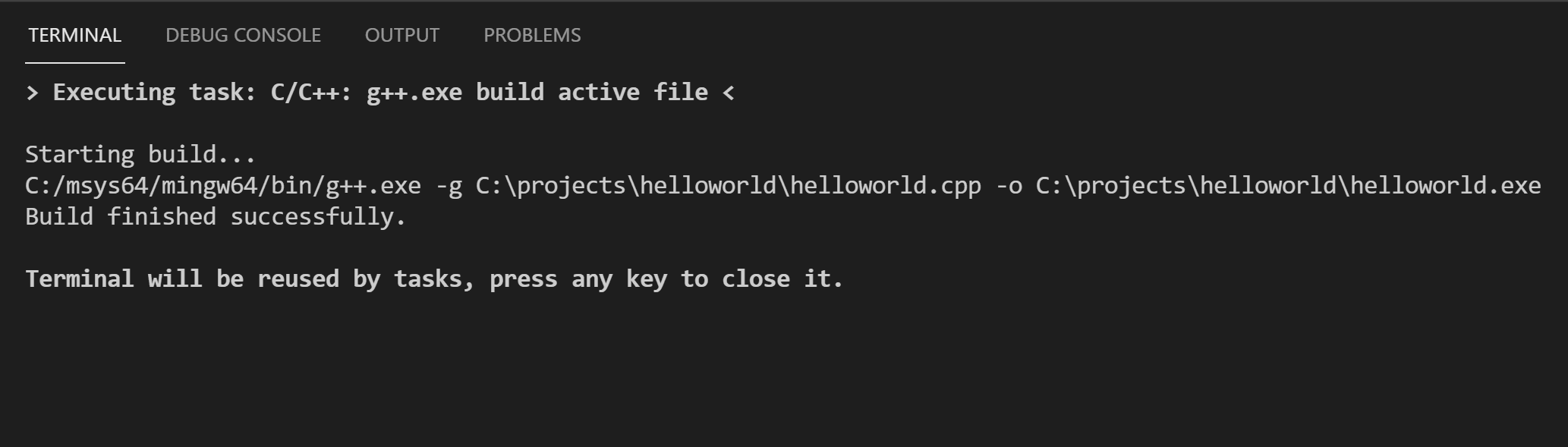
When the task starts, y'all should see the Integrated Final panel appear beneath the source code editor. After the task completes, the concluding shows output from the compiler that indicates whether the build succeeded or failed. For a successful g++ build, the output looks something similar this:
-
Create a new last using the + button and you'll have a new terminal with the
helloworldfolder equally the working directory. Rundirand you should at present encounter the executablehelloworld.exe.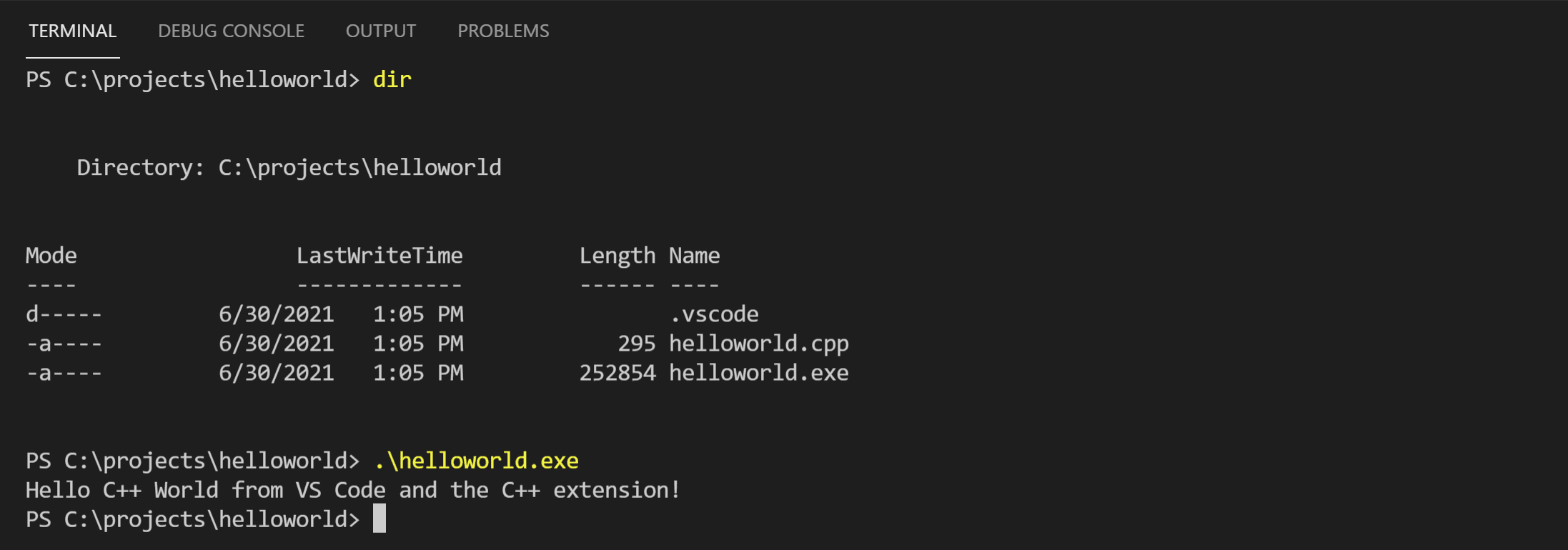
-
You can run
helloworldin the final by typinghelloworld.exe(or.\helloworld.exeif you apply a PowerShell final).
Note: Y'all might need to press Enter a couple of times initially to run across the PowerShell prompt in the terminal. This result should be fixed in a futurity release of Windows.
Modifying tasks.json
You lot can modify your tasks.json to build multiple C++ files by using an statement like "${workspaceFolder}\\*.cpp" instead of ${file}. This will build all .cpp files in your current binder. You can also change the output filename by replacing "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe" with a difficult-coded filename (for case "${workspaceFolder}\\myProgram.exe").
Debug helloworld.cpp
Next, you lot'll create a launch.json file to configure VS Code to launch the GDB debugger when y'all printing F5 to debug the plan.
- From the principal bill of fare, choose Run > Add Configuration... and so choose C++ (GDB/LLDB).
- You'll and so see a dropdown for various predefined debugging configurations. Cull k++.exe build and debug active file.
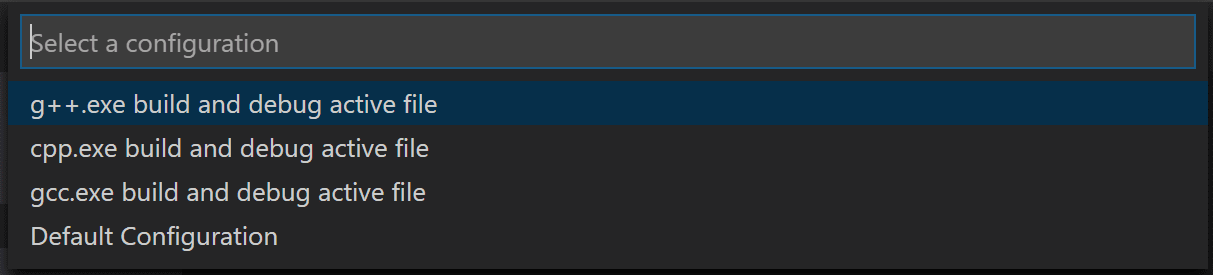
VS Code creates a launch.json file, opens it in the editor, and builds and runs 'helloworld'.
{ "version" : "0.ii.0" , "configurations" : [ { "name" : "thou++.exe - Build and debug active file" , "blazon" : "cppdbg" , "request" : "launch" , "programme" : "${fileDirname} \\ ${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe" , "args" : [], "stopAtEntry" : false , "cwd" : "${fileDirname}" , "environment" : [], "externalConsole" : imitation , "MIMode" : "gdb" , "miDebuggerPath" : "C: \\ msys64 \\ mingw64 \\ bin \\ gdb.exe" , "setupCommands" : [ { "clarification" : "Enable pretty-press for gdb" , "text" : "-enable-pretty-printing" , "ignoreFailures" : truthful } ], "preLaunchTask" : "C/C++: g++.exe build active file" } ] } The program setting specifies the programme y'all want to debug. Hither information technology is set to the active file binder ${fileDirname} and active filename with the .exe extension ${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe, which if helloworld.cpp is the active file will be helloworld.exe.
By default, the C++ extension won't add any breakpoints to your source lawmaking and the stopAtEntry value is set up to fake.
Change the stopAtEntry value to true to crusade the debugger to cease on the chief method when yous start debugging.
Note: The
preLaunchTasksetting is used to specify job to be executed earlier launch. Make sure it is consistent with thetasks.jsonfilelabelsetting.
Start a debugging session
- Go dorsum to
helloworld.cppand so that it is the active file. - Press F5 or from the main menu choose Run > Start Debugging. Before you start stepping through the source lawmaking, permit'south take a moment to discover several changes in the user interface:
-
The Integrated Terminal appears at the bottom of the source code editor. In the Debug Output tab, you see output that indicates the debugger is upward and running.
-
The editor highlights the showtime statement in the
mainmethod. This is a breakpoint that the C++ extension automatically sets for you: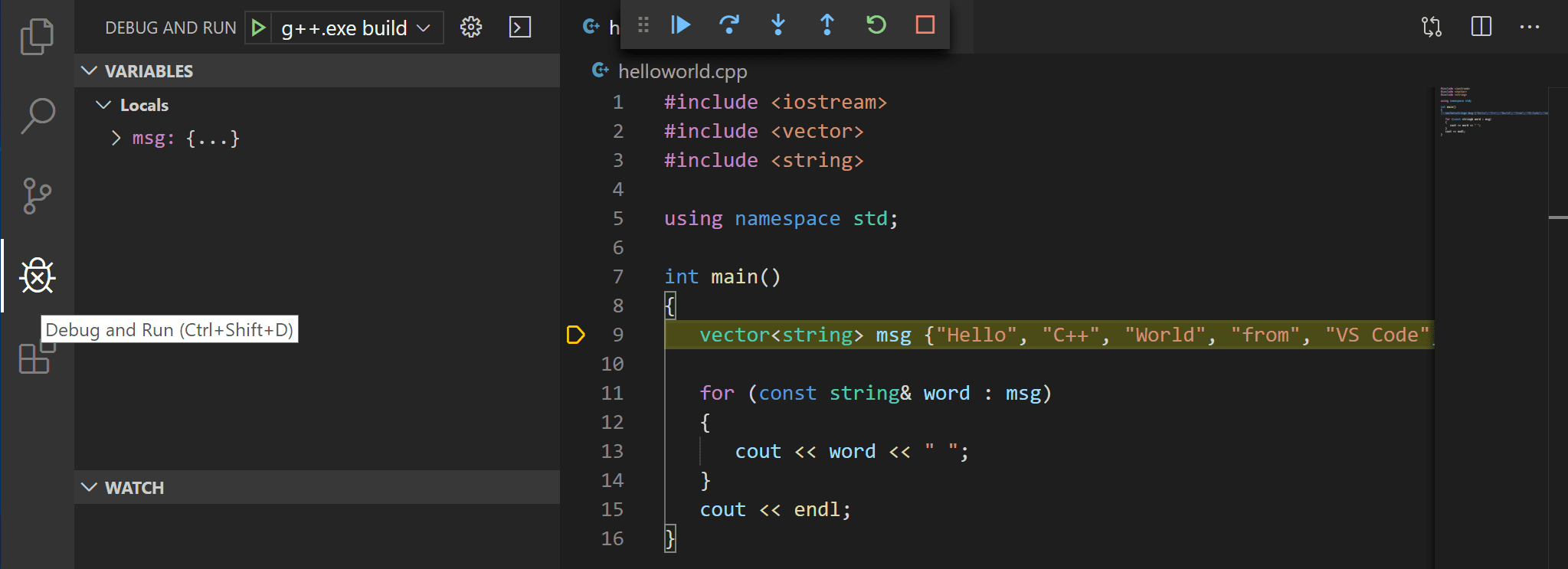
-
The Run view on the left shows debugging information. You'll see an instance later in the tutorial.
-
At the top of the code editor, a debugging control panel appears. You can move this around the screen past grabbing the dots on the left side.
Step through the code
Now you're ready to start stepping through the code.
-
Click or printing the Step over icon in the debugging control panel.
This will advance program execution to the first line of the for loop, and skip over all the internal office calls within the
vectorandstringclasses that are invoked when themsgvariable is created and initialized. Notice the alter in the Variables window on the left.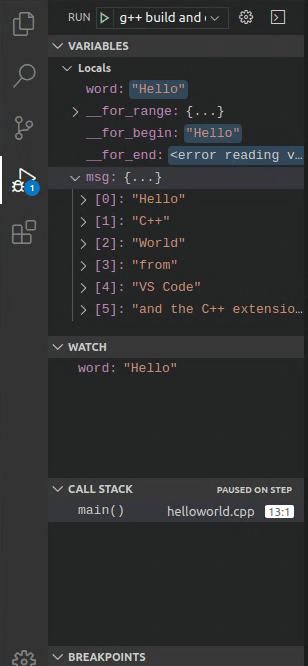
In this case, the errors are expected because, although the variable names for the loop are now visible to the debugger, the statement has not executed even so, and then at that place is zip to read at this bespeak. The contents of
msgare visible, withal, because that statement has completed. -
Press Step over once again to accelerate to the next statement in this plan (skipping over all the internal code that is executed to initialize the loop). Now, the Variables window shows information about the loop variables.
-
Press Step over once more to execute the
coutstatement. (Notation that every bit of the March 2022 release, the C++ extension does not impress any output to the Debug Console until the loop exits.) -
If you like, you can keep pressing Footstep over until all the words in the vector take been printed to the console. Merely if you are curious, endeavor pressing the Stride Into button to footstep through source code in the C++ standard library!
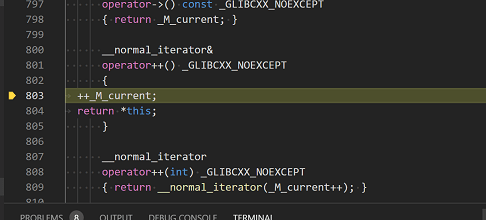
To render to your ain code, one manner is to keep pressing Step over. Another way is to set a breakpoint in your code by switching to the
helloworld.cpptab in the code editor, putting the insertion point somewhere on thecoutstatement inside the loop, and pressing F9 . A cherry dot appears in the gutter on the left to indicate that a breakpoint has been assail this line.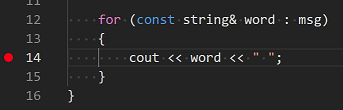
And then press F5 to showtime execution from the current line in the standard library header. Execution will break on
cout. If you similar, you lot can press F9 again to toggle off the breakpoint.When the loop has completed, you tin see the output in the Integrated Terminal, along with another diagnostic information that is output by GDB.

Set a watch
Sometimes you might want to keep track of the value of a variable equally your plan executes. You can practise this by setting a watch on the variable.
-
Place the insertion point within the loop. In the Lookout window, click the plus sign and in the text box, type
word, which is the name of the loop variable. Now view the Picket window every bit you step through the loop.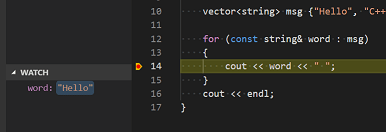
-
Add some other watch by adding this argument earlier the loop:
int i = 0;. Then, inside the loop, add this statement:++i;. At present add a sentinel forias y'all did in the previous step. -
To chop-chop view the value of whatsoever variable while execution is paused on a breakpoint, you tin hover over information technology with the mouse arrow.
C/C++ configurations
If y'all want more than control over the C/C++ extension, you can create a c_cpp_properties.json file, which volition permit you to alter settings such every bit the path to the compiler, include paths, C++ standard (default is C++17), and more.
You lot can view the C/C++ configuration UI by running the control C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI) from the Control Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)).
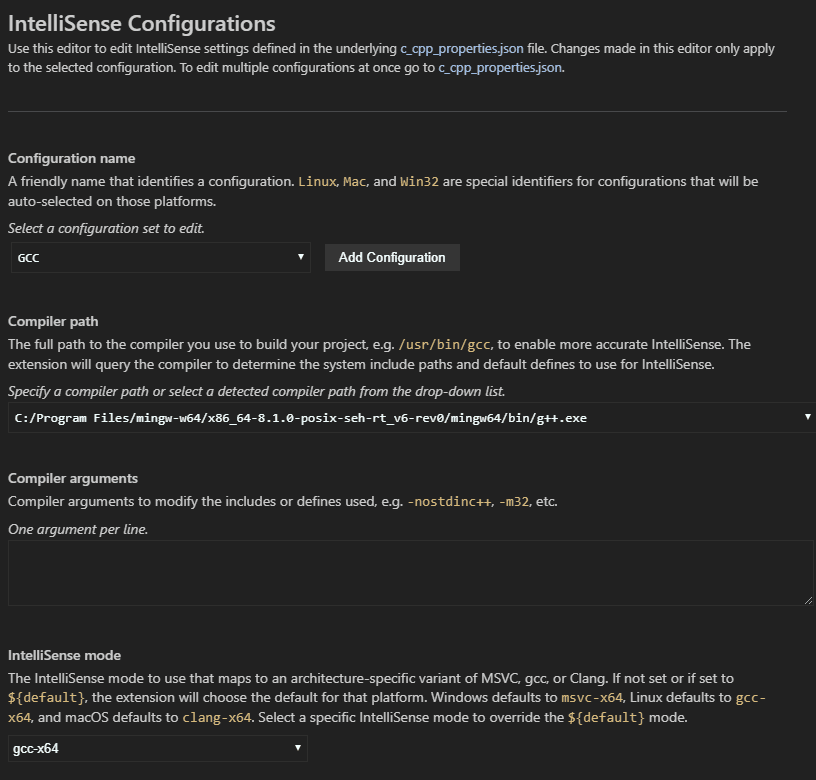
This opens the C/C++ Configurations page. When you lot make changes here, VS Code writes them to a file called c_cpp_properties.json in the .vscode folder.
Hither, nosotros've changed the Configuration proper noun to GCC, set the Compiler path dropdown to the g++ compiler, and the IntelliSense mode to lucifer the compiler (gcc-x64)
Visual Studio Code places these settings in .vscode\c_cpp_properties.json. If you open that file directly, it should wait something similar this:
{ "configurations" : [ { "name" : "GCC" , "includePath" : [ "${workspaceFolder}/**" ], "defines" : [ "_DEBUG" , "UNICODE" , "_UNICODE" ], "windowsSdkVersion" : "10.0.18362.0" , "compilerPath" : "C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/g++.exe" , "cStandard" : "c17" , "cppStandard" : "c++17" , "intelliSenseMode" : "windows-gcc-x64" } ], "version" : iv } Yous simply demand to add to the Include path array setting if your program includes header files that are not in your workspace or in the standard library path.
Compiler path
The extension uses the compilerPath setting to infer the path to the C++ standard library header files. When the extension knows where to observe those files, it can provide features similar smart completions and Go to Definition navigation.
The C/C++ extension attempts to populate compilerPath with the default compiler location based on what it finds on your system. The extension looks in several common compiler locations.
The compilerPath search order is:
- Kickoff check for the Microsoft Visual C++ compiler
- Then look for g++ on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- Then chiliad++ for Mingw-w64.
If you have Visual Studio or WSL installed, y'all may need to change compilerPath to match the preferred compiler for your project. For example, if you installed Mingw-w64 version 8.1.0 using the i686 compages, Win32 threading, and sjlj exception handling install options, the path would await like this: C:\Program Files (x86)\mingw-w64\i686-8.1.0-win32-sjlj-rt_v6-rev0\mingw64\bin\g++.exe.
Troubleshooting
MSYS2 is installed, but g++ and gdb are however not plant
You must follow the steps on the MSYS2 website and use the MSYS CLI to install Mingw-w64, which contains those tools.
MinGW 32-chip
If yous need a 32-bit version of the MinGW toolset, consult the Downloading section on the MSYS2 wiki. It includes links to both 32-bit and 64-bit installation options.
Side by side steps
- Explore the VS Code User Guide.
- Review the Overview of the C++ extension.
- Create a new workspace, copy your
.vscodeJSON files to it, adjust the necessary settings for the new workspace path, program name, and then on, and outset coding!
How To Set Up Visual Studio Code For C++,
Source: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/config-mingw
Posted by: gordonbral1986.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Set Up Visual Studio Code For C++"
Post a Comment